The fourth industrial revolution - intelligent and flexible production. Combining technological innovations from the field of robotics, artificial intelligence, sophisticated sensors, cloud computing, big data analytics and internet of things has evolved into Industry 4.0.
What would our world be without machines, without computer, without even the simplest technologies that we use every die? How would we be able to communicate, to move from point to point, gain store and prepare our food?
Most of the products that people in the industrialized nations use today are brought to the market by the process of mass production, by people, machines or robots. People of ancient and medieval times had no such products. They had to spend long, tedious hours of hand labor even on simple objects.
But then during the late 18th and early 19th centuries in Britain begins the First Industrial Revolution and world is going to change into the one we know it today.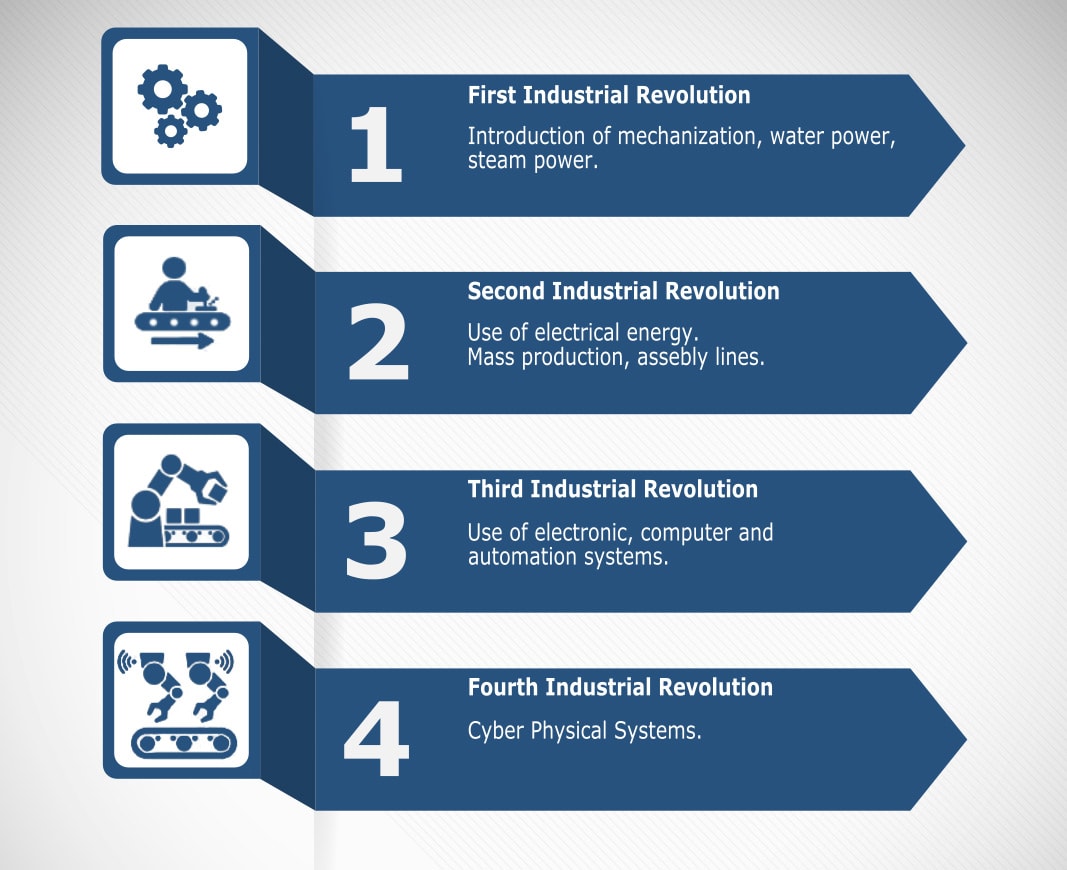
Industrial revolutions
The first industrial revolution (1.0) involved the mechanization of production and converting water to steam power. The second industrial revolution (2.0) tooks place 30 years later when the first electricity-powered assembly line introduces mass production. The third industrial revolution (3.0) starts in the late 1960s when the first programmable logistic controller (PLC) enables production automation through the use of electronic and IT systems.
The term Industry 4.0, originally called “Industrie 4.0”, comes from Germany. In 2011 at the Hannover Messe trade fair it is introduced for the first time by the German federal government. And a little bit later Industry 4.0 is pointed as one of the future projects adopted in the „Action Plan High-tech strategy 2020“. The Federal Government thereby addresses the rapid social and technological development in this area and puts structures for cooperation between all actors of innovation in Germany.
According to Germany Trade and Invest (GTAI) Industry 4.0 refers to the technological evolution from embedded systems to cyber-physical systems: “Industrie 4.0 connects embedded system production and smart production processes to pave the way to a new technological age which will radically transform industry and production value chains and business model”.
Industry 4.0 is also called ‘smart industry’, ‘intelligent industry’, ‘smart factory’ or ‘smart manufacturing’. In many senses it is related to the Industrial Internet and since 2016 the Industrial Internet Consortium and Industry 4.0 platform, “Plattform Industrie 4.0”, indeed start collaborating. The “Plattform Industrie 4.0” itself aims in securing and developing Germany’s top international position in industrial manufacturing.
Industry 4.0 involves Internet of Things (IoT) and relevant physical technologies, including analytics, additive manufacturing, robotics, artificial intelligence and cognitive technologies, advanced materials, and augmented reality that complete the merging of physical and digital objects. It combines also production methods with state-of-the-art information and communication technology. The driving force behind this development is the rapidly increasing digitalization of the economy and society.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is maybe the core element of Industry 4.0. The IoT concept has gained traction in recent years as the importance of connectivity—both in creating products and services and increasing satisfaction among customers and clients has become better understood leading to the rapidly advancing of the connected technologies.
The IoT networks intelligent systems with each other, which makes largely self-managing production processes possible: In the world of Industry 4.0, people, machines, equipment, logistics systems and products communicate and cooperate with each other directly. Automated processes in the production and logistics are integrated intelligently beyond company boundaries making manufacturing more adaptable and profitable.
The manufacturing companies have to deal with the upcoming changes in order to stay up-to-date and to response adequately to the future technologies and to the “smart factory” demands by implementing or upgrading and adjusting the company processes.
Another factor to be concerned is the shifting of manufacturing to information-based economy and this is again possible through the increased connectivity and ever more sophisticated data-gathering and analytics capabilities enabled by the Internet of Things.
This simplifies the creation of chains which can trace the lifecycle of a single product. From the initial product idea and development, production, use and maintenance through to recycling. This enables companies to produce products that are customized according to individual customer requirements more easily than before. Individualizing production and maintenance of products can change the world norms and standards.
Networking the companies in the supply and logistics chain to a global real-time information database will also reduce the manufacturing costs as it enables the manufacturers to react faster and adequately to the market changes. Production processes can be controlled beyond company boundaries to save resources and energy and so increase profit.
As the economy becomes more digitized and networked, the number of interfaces between different market participants will increase. Uniform standards for different industry sectors, IT security and data protection, as well as questions relating to the way work will be organized in the future are yet to come.
References
Germany Trade & Invest www.gtai.de
Platform Industrie 4.0 www.plattform-i40.de
Industrial Internet Consortium IIC www.iiconsortium.org



0 COMMENTS //
Join the discussion