
The “Analog signals” are continuously varying representation of a condition, physical phenomenon, or quantity such as flow, pressure, or temperature, transmitted as electrical, mechanical, or pneumatic energy.
The “Analog signals” are continuously varying representation of a condition, physical phenomenon, or quantity such as flow, pressure, or temperature, transmitted as electrical, mechanical, or pneumatic energy. Voltage and current are easy to measure, manipulate, and transmit over long distances, that is why they are widely used to represent such physical values. To transform these physical values into electrical signals, appropriate sensors should be used. If the sensor is connected to measuring transmitter, then the measured signal can be transformed into a normed-measuring signal. The measuring transmitter may be integrated in the casing of the sensor. The further transmission of electrical signals happens over electrical wires. Signal coming from a sensor, can be forwarded to devices like:
- Gauge.
- Display.
- Regulator.
- Converter or amplifier.
In the common practice an analog signal is going to pass the following stations:
- It reacts on the state or changes of physical value and transforms this value into an evaluable electric signal. The sensor generates voltage in the electrical circuit or it causes voltage drop in a constant current electrical circuit.
- Usually the sensor is connected electrically to another interface-module, which “prepares” the signal. These modules may be used to:
- Amplifying, filtering and norming of the measured signal.
- Galvanic isolation of the measuring circuit.
- Supplying power to the sensor.
- The transformed signal is going to be forwarded to device or devices which can evaluate the signal. This can be display, PLC, DCS…
- As addition the analogue signal can be digitalized and transferred over bus. The information flow in modern control systems in transferred over bus-connections. They allow huge flows of information over to be transferred over limited amount of electrical connections. To transfer the analog signal over bus-system, the analogue signal should be digitalized.
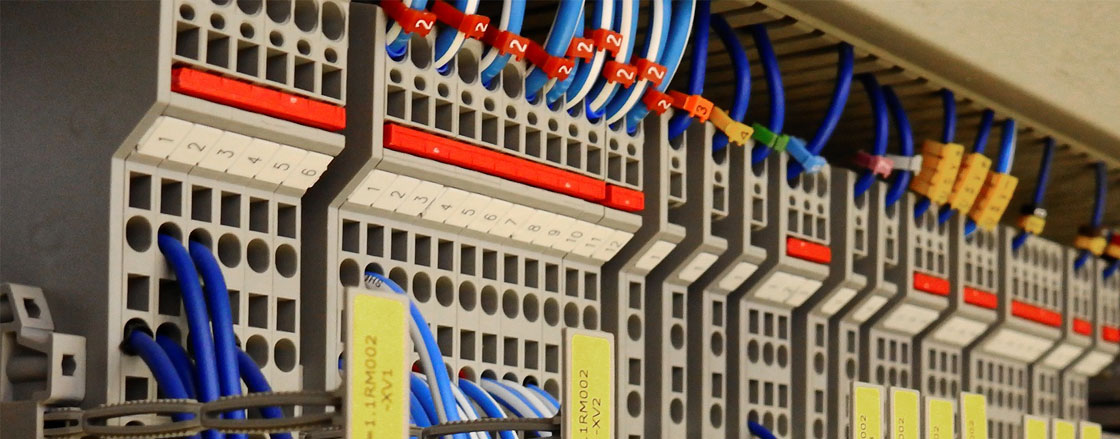
In the core of the “Controls and Instrumentation” technology is the acquisition, processing and evaluation of signals coming from the environment, machine or process.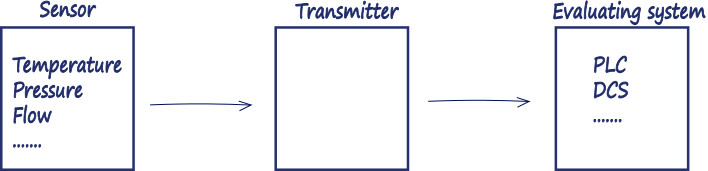
Figure 1. Processing of signals.
The sensor performing the measurement. To control a dynamic variable in a process, information about the entity or variable is needed. This information is obtained by measuring the variable. Measurement refers to the conversion of the process variable into an analog or digital signal that can be used by the control system. Transmitters are devices used to amplify and format signals so that they are suitable for transmission over long distances with zero or minimal loss of information. The transmitted signal can be in one of the several formats, i.e., pneumatic, digital, analog voltage, analog current, or as a radio frequency (RF) modulated signal. Digital transmission is preferred in newer systems because the controller is a digital system, and as analog signals can be accurately digitized, digital signals can be transmitted without loss of information.
Signal transmission is needed when the observation or application point of the output of a measurement system is some distance away from the site of the primary transducer. Sometimes, this separation is made only for convenience, but more often, it follows from the physical inaccessibility or environmental unsuitability of the site of the primary transducer for mounting the signal presentation/recording unit.
In the evaluation step of the process control sequence, the measurement value is examined, compared with the desired value or set point, and the amount of corrective action needed to maintain proper control is determined. A device (controller) performs this evaluation. The controller
can be a pneumatic, electronic, or mechanical device mounted in a control panel or on the process equipment. It can also be part of a computer control system, in which case the control function is performed by software.
The control element in a control loop is the device that exerts a direct influence on the process or manufacturing sequence. This final control element accepts an input from the controller and transforms it into some proportional operation that is performed on the process. In most cases, this final control element will be a control valve, electrical motor, pump.
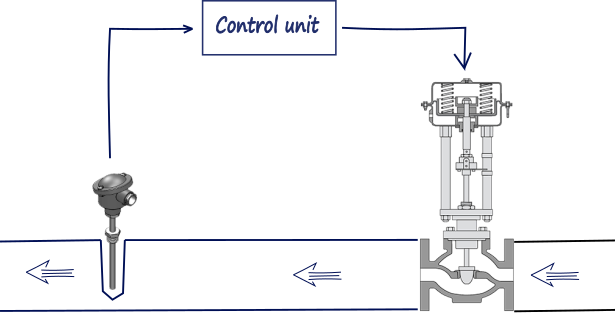
Figure 2. Measured signal in the control system.



0 COMMENTS //
Join the discussion